- The Faculty
- Academic
- Postgraduate
- Directorates
- Self-Evaluation
- Transparency
- Continuing Education
Health Area
Promote the continuous improvement of the physical, psychosocial, and environmental conditions in which students, teachers, administrative staff, and graduates develop through the execution of formative, preventive, and corrective activities that impact on quality of life and healthy habits.
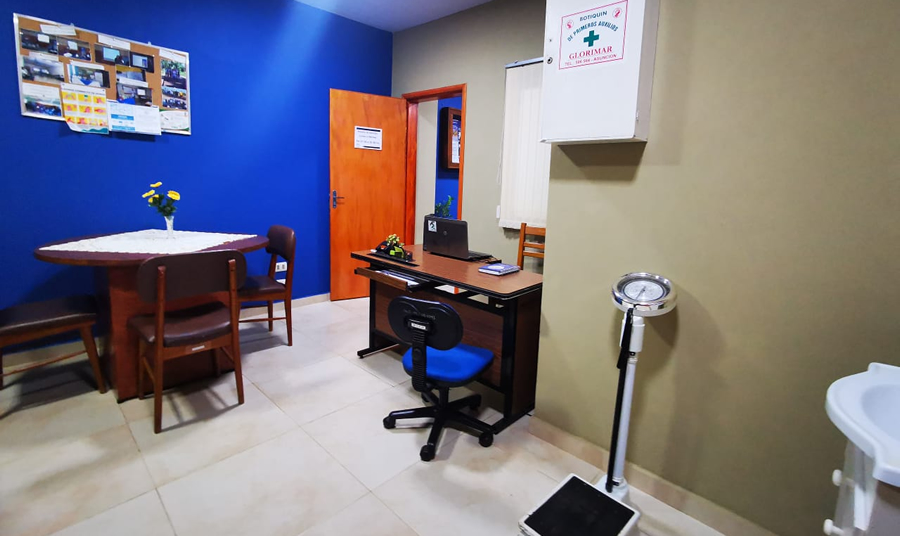
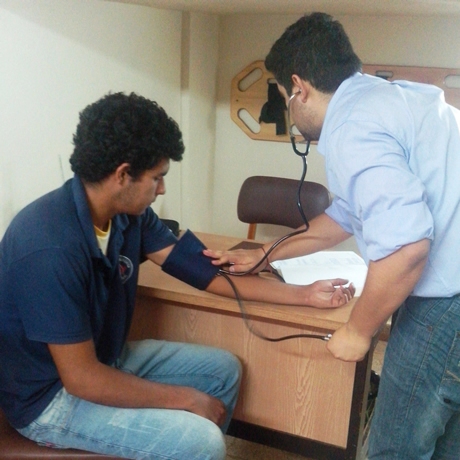


Students, teachers, and staff are provided care within the institution in an equipped Nursing room in which medications that do not require a medical prescription, minor cures, and blood pressure measurements are available, as well as nutritional evaluation and minor emergency care
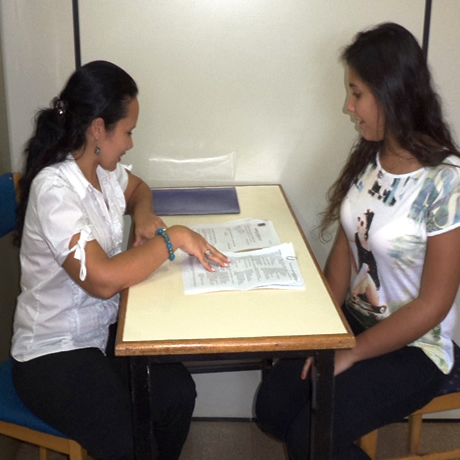

Academic excellence is sought, which implies not only physical firmness, but also mental and social; Therefore, attention is available with trained psychologists, favoring the improvement of the quality of life of students, teachers and officials through the interventions of psychology.
The use of physiotherapy within the Polytechnic Faculty is based on the use of physical agents such as massage, movement, heat, cold, etc. used for the procedure of minor injuries, which may be caused after some physical activity or work stress.
Hormonal, lifestyle, and environmental factors have been identified that can increase the risk of breast cancer. However, it is not clear why some people without risk factors develop cancer while others with risk factors never do. Breast cancer is likely caused by a complex interaction of genetic composition and the environment.
The signs and symptoms of breast cancer may include the following:
- A breast lump or thickening that feels different from the surrounding tissues
- Change in size, shape, or appearance of a breast
- Changes in the skin of the breast, such as dimpling
- Recent nipple inversion
- Excoriation, scaling, crusting, or peeling of the pigmented skin area surrounding the nipple (areola) or the skin of the breast
- Redness or indentations in the skin of the breast, like the skin of an orange
The factors associated with an increased risk of breast cancer are the following:
- Being female. Women are much more likely than men to develop breast cancer.
- Advanced age. The risk of breast cancer increases as you get older.
- Personal history of breast conditions. If you have had a breast biopsy that revealed lobular carcinoma in situ or atypical hyperplasia of the breast, you have a high risk of developing breast cancer.
- Personal history of breast cancer. If you had cancer in one breast, your risk of getting cancer in the other breast is higher.
Family history of breast cancer. If your mother, sister, or daughter has been diagnosed with breast cancer, particularly at a young age, your risk of getting breast cancer is higher. However, most people who are diagnosed with breast cancer do not have a family history of the disease.
Hereditary genes that increase the risk of breast cancer. Certain genetic mutations that increase the risk of breast cancer can be passed down from parents to children. The most well-known genetic mutations are known as "BRCA1" and "BRCA2". These genes can greatly increase your risk of getting breast cancer and other types of cancer, but do not make cancer inevitable.
Exposure to radiation. If you received radiation treatments to the chest in childhood or early adulthood, your chances of getting breast cancer are higher.
Obesity. Being obese increases the risk of getting breast cancer.
Starting menstruation at an early age. Starting your first period before age 12 increases the risk of getting breast cancer.
Starting menopause at a later age. If menopause started at a later age for you, you are more likely to get breast cancer.
Having your first child at a later age. Women who have their first child after age 30 may have a higher risk of getting breast cancer.
Never having been pregnant. Women who have never been pregnant have a higher risk of getting breast cancer than women who have had one or more pregnancies.
Postmenopausal hormonal therapy. Women who take medications for hormonal therapy that combine estrogen and progesterone to treat signs and symptoms of menopause have a higher risk of getting breast cancer. The risk of getting breast cancer decreases when women stop taking these medications.
Consuming alcohol. Drinking alcohol increases the risk of getting breast cancer.
Treatment: The mainstays of treatment are surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and chemotherapy, which will be decided by cancer specialists.
For more information, please contact the National Program for Prevention and Early Detection of Cervical and Breast Cancer through email: pnpcacum@hotmail.com
 Diabetes is a disease that occurs when the level of glucose (sugar) in the blood is high. Glucose comes from food and is the main source of energy for the bodys cells to perform all their functions.
Diabetes is a disease that occurs when the level of glucose (sugar) in the blood is high. Glucose comes from food and is the main source of energy for the bodys cells to perform all their functions.
Diabetes occurs when the insulin (bodys natural hormone) secreted by the pancreas is insufficient; therefore, excess free glucose accumulates in the blood and the bodys cells have no energy.
In chronic cases, excess glucose in the blood causes serious health problems, which is why diabetes is known as the "silent killer" due to the absence of signs and symptoms in the early years.
Diabetes cannot be cured; diabetes is controlled. The patient must follow the instructions of their multidisciplinary health team.
The normal values of venous blood glucose are between 70 and 99 mg/dl. Values between 100 and 125 mg/dl are called prediabetes, and any value equal to or greater than 126 mg/dl is considered diabetes. The values in pregnant women differ from these parameters. These values must be evaluated by the doctor to certify the diagnosis and start timely treatment, avoiding complications.
The main types of diabetes are type 1, type 2, and gestational (during pregnancy).
Type 1 diabetes
It corresponds to less than 10% of cases and is not preventable; here, the pancreas does not produce insulin at all. This is because the bodys defense system attacks the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas and destroys them. Type 1 diabetes is common in pediatric and young adult ages. These patients depend on the application of external injectable insulin 6 times a day, in addition to capillary glucose monitoring between 5 to 8 controls before meals.
Type 2 diabetes
It is the most frequent, representing 90% of cases. IT IS PREVENTABLE. Here, insulin does not work properly due to excesses in diet, sedentary lifestyle, toxic habits, overweight, and obesity. It can appear at any age, even during childhood. However, this type of diabetes occurs most frequently in middle-aged and geriatric people. Treatment begins with the modification of nutritional habits, inclusion of physical activity recommended by the doctor (frequency, periodicity, and type of activity), and suspension of toxic habits. Subsequently, treatment is intensified with oral antidiabetic drugs and the use of external insulin, according to the doctors prescription.
Gestational (during pregnancy)
It can appear from the beginning to the end of pregnancy. Once pregnancy is confirmed, periodic glycemia controls are recommended to detect the pathology in time. High glycemia during pregnancy leads to complications in fetal development and growth, problems during childbirth, and predisposes the newborn to noncommunicable chronic diseases in adulthood.
Complications
Elevated and sustained blood glucose levels can cause complications throughout the body, from head to toe.
The most feared complications are stroke, cognitive impairment, blindness, deafness, heart attack, kidney failure, sexual dysfunction, non-healing wounds, diabetic neuropathy, leg amputation, among others.
All diabetes complications are PREVENTABLE if the patient and a family member attend medical consultations early and periodically, fully complying with the instructions of their multidisciplinary healthcare team. Irregularity, passivity, treatment abandonment, as well as the absence of family support, are predisposing factors for the appearance of complications, which are often irreversible.
Symptoms
The following symptoms should alert the patient and their family: frequent thirst with a preference for sugary drinks, voracious hunger, unexplained weight loss, frequent urination that wakes them up at night, fatigue that does not improve with rest, itching of the skin and genital area, non-healing wounds, blurry vision, erectile dysfunction, numbness or tingling of the feet and legs, as well as depression. In the presence of 2 or more symptoms, it is recommended to seek medical attention for clinical and laboratory monitoring.
Diabetes in Paraguay
The following figures correspond to the survey conducted in 2011 by the Directorate of Non-Communicable Chronic Diseases of the Ministry of Public Health.
9.7% of the general population in Paraguay has diabetes. Of the total population, 7.9% corresponds to males and 11% to females, respectively. The predominant age group is between 45 and 75 years old.
 Arterial hypertension or "high blood pressure" is characterized by persistent elevation of blood pressure to levels equal to or greater than 140/90 mmHg. It is known as the "silent killer", since it rarely causes symptoms.
Arterial hypertension or "high blood pressure" is characterized by persistent elevation of blood pressure to levels equal to or greater than 140/90 mmHg. It is known as the "silent killer", since it rarely causes symptoms.
Why is arterial hypertension dangerous?
The higher the blood pressure, the greater the risk of damage to the heart and blood vessels of major organs such as the brain and kidneys. Hypertension is the worlds most important preventable cause of cardiovascular disease and stroke.
If left uncontrolled, hypertension can cause a heart attack, an enlargement of the heart, and eventually heart failure. Blood vessels can develop bulges (aneurysms) and weak areas that make them more susceptible to blockage and rupture. Blood pressure can cause blood to leak into the brain and cause a stroke. It can also cause kidney failure, blindness, and cognitive decline.
Symptoms
Sometimes, hypertension causes symptoms such as headaches, shortness of breath, dizziness, chest pain, heart palpitations, and nosebleeds, but not always.
Prevention
High blood pressure can be prevented and controlled through a healthy lifestyle.
Everyone, regardless of age, can take measures to lower the risk of hypertension and therefore heart disease. A healthy diet and daily physical activity, including outdoor play, and reducing TV time are the best ways to stay healthy.
Reducing salt intake, as well as sugary drinks, increasing the intake of fruits, vegetables, dairy, and white meats also contribute to prevention.
The recommended daily salt consumption per person is up to 5 grams, equivalent to a level teaspoon (teaspoon); choosing fresh foods instead of processed ones, thus selecting healthier alternatives.
It is also important to avoid tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption.
All adults should have their blood pressure measured periodically, as it is important to know the values. If it is elevated, medical consultation is necessary, as lifestyle changes alone may not be sufficient for some people, they may also need medication that must be prescribed by a doctor.
Adults can contribute to treatment by taking prescribed medication, changing their lifestyle, and monitoring their health.
People with hypertension who also have a high blood sugar level, hypercholesterolemia, or renal insufficiency are at an even greater risk of myocardial infarction or stroke. Therefore, it is important to have periodic checks on the amount of sugar and cholesterol in the blood and the level of albumin in the urine.
Children should have their blood pressure checked
A study carried out by the National Cardiovascular Control Program in 2015 in educational institutions in the country found that 3.2% of children and adolescents aged between 8 and 15 years had high blood pressure for their age. Therefore, blood pressure measurement in children is being progressively implemented in health centers under the Ministry of Public Health, starting from the age of 5, especially in children who are overweight or have a family history of hypertension.
National figures
The country currently has a prevalence of hypertensive patients of approximately 46.8%, meaning that 5 out of 10 Paraguayans have high blood pressure, with this figure concentrated in the population aged 30 to 60 years; the highest peak is seen in the over 55 age group.
 Smoking is the addiction to tobacco, mainly caused by one of its most active components: nicotine, which acts on the central nervous system.
Smoking is the addiction to tobacco, mainly caused by one of its most active components: nicotine, which acts on the central nervous system.
Tobacco products are those made entirely or partially from tobacco, whether for smoking, chewing, snuffing, or dipping. All of them contain nicotine, a highly addictive psychoactive ingredient.
Consequences of tobacco use
It has been scientifically proven that smoking harms health, promoting the appearance of various disorders and illnesses, such as heart attacks (infarctions), strokes, chronic bronchitis, lung diseases, and other related diseases.
Smoking also contributes to sexual impotence, the development of stomach and duodenal ulcers, osteoporosis, and various types of cancer (lung, oral, laryngeal, pharyngeal, esophageal, stomach, kidney, pancreas, liver, bladder, cervical, colon, and rectal) and a type of leukemia. It predisposes to decreased vision. Smokers have less immunity to infections than non-smokers.
All of these diseases can affect both the active smoker and the person exposed to secondhand tobacco smoke (passive smoker).
Effects over a lifetime:
Children exposed during intrauterine life to tobacco smoke toxins through maternal smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke often present with reduced growth and lung function. Young children exposed to secondhand smoke are at risk of developing asthma and exacerbations of it, pneumonia and bronchitis, as well as frequent infections of the lower respiratory tract. Smokers should never smoke in the presence of infants or young children.
Air pollution:
Tobacco smoke is a dangerous form of air pollution in enclosed spaces: it contains more than 7,000 chemical substances, 69 of which are known to be carcinogenic. Although smoke can be invisible and odorless, it can remain in the air for up to five hours.
Vaping, gateway to smoking
Vaping is the route being used by tobacco industries to attract more consumers, through the use of the electronic cigarette, a trend that is becoming more popular among young people, especially those who start smoking.
The electronic cigarette is becoming the gateway to smoking. The appeal of vape devices is the flavoring added by manufacturers, from which the nicotine aerosol is generated, making initial exposures more pleasant, improving the appeal to first-time users.
Quitting smoking is possible
Smokers who want to quit smoking can go to pulmonology clinics, where tobacco cessation treatment is provided. The care is free and personalized.
The Ministry of Health has pulmonology clinics authorized for tobacco cessation, which are located in INERAM, as well as in the hospitals of Encarnación, Villarrica, Santa Rosa del Aguaray, and the Materno Infantil of San Lorenzo (Calle´i). Also, in Concepción, Villa Hayes, Ciudad del Este, in San Juan and San Ignacio - Misiones, in Caazapá, Caacupé, Pilar, Salto del Guairá, and San Estanislao.
Smoking in Paraguay
12.2% of all deaths in the country can be attributed to smoking, with 3,354 preventable deaths per year.
National figures reveal that about 1,200 people die each year in traffic accidents, while the number of deaths associated with tobacco consumption is three times higher.
In Paraguay, lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death. In 2018 alone, 733 deaths were recorded due to this disease, according to data from the National Cancer Program.
The Ministry of Health emphasizes that smoking kills up to half of its consumers, and urges smokers to quit this habit and choose a healthy life.
Other diseases that result from this habit include cardiovascular disease, stroke, pneumonia, and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD).

 Daily consumption of both raw and cooked vegetables, with lunch and dinner, is very important, as is the intake of at least three fruits every day (especially seasonal fruits).
Daily consumption of both raw and cooked vegetables, with lunch and dinner, is very important, as is the intake of at least three fruits every day (especially seasonal fruits).
It is healthy to eat dry legumes and opt for lean meats.
To protect the heart, it is essential to reduce the consumption of salt, fried foods, and fats.
Consuming fewer sweets, sodas, and sugary drinks is also essential for maintaining good health.
Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages is harmful to health and can cause accidents.
Drinking at least 8 glasses of water during the day is essential for proper body function.

Mental health is defined as a state of well-being in which the individual:

Habits that help maintain not only a healthy body but also a healthy mind:

 Regular physical activity provides numerous health benefits. The regular practice of exercise or sports helps reduce the occurrence of risk factors for the development of chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, some cancers, osteoporosis, high blood pressure, and other pathologies. It also helps to maintain a healthy weight and thus improve peoples quality of life.
Regular physical activity provides numerous health benefits. The regular practice of exercise or sports helps reduce the occurrence of risk factors for the development of chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, some cancers, osteoporosis, high blood pressure, and other pathologies. It also helps to maintain a healthy weight and thus improve peoples quality of life.
Options for promoting physical activity in daily life:
To enjoy all the benefits that regular physical activity provides, it is recommended to:
| ACTIVITIES OFFERED TO THE COMMUNITY OF THE POLYTECHNICAL FACULTY | |
|---|---|
 |
Vacunación y charla sobre enfermedades respiratoriasLa comunidad académica de la Facultad Politécnica UNE fue beneficiada de una jornada de vacunación y una charla titulada... |
 |
Evaluación Nutricional en la FPUNEEn el marco del programa de Bienestar Social Universitario, específicamente en el sub programa Calidad de Vida, se realizó el día jueves 30 de mayo del corriente año.... |
 |
Campaña de Vacunación FPUNE 2017 |
 |
Taller de Pausas Activas a funcionarios de la Facultad Politécnica |
 |
Hábitos y Estilos de vida saludable |
 |
Charla de Prevención del VIH/ SIDA |
 |
Charlas de Habito Saludable |
 |
Caminatas al aire libre y ejercicios de relajación |
 |
Jornada de Capacitación en Primeros Auxilios y Prevención de Incendios |
 |
Charlas de Prevención sobre Dengue, Chikungunya y Zika |
 |
Campaña de Vacunación |
 |
Charla sobre Violencia Intrafamiliar |

La encargada de Salud y Seguridad Ocupacional de la Facultad Politécnica de la Universidad Nacional del Este, mediante el área de Salud y Seguridad Ocupacional, ha iniciado una campaña de información y sensibilización respecto de la gestión de prevención de accidentes denominada “Charla de 5 Minutos de Educación Preventiva” que consiste en charlas de suma importancia para los miembros de la comunidad educativa, la cual contempla beneficios en eficiencia y productividad que consiste en diálogos breves antes o durante una jornada diaria. Para lo cual se elaboraron materiales didácticos que ponemos a disposición del público interno y externo en nuestra página web y redes sociales.